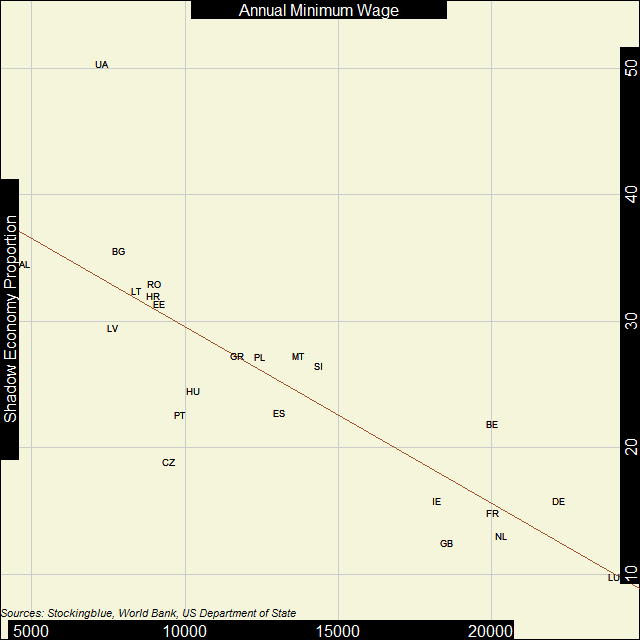
In Europe, the inverse correlation between the strength of the shadow economy and the minimum wage is very strong. As the shadow economy weakens, the minimum wage tends to be higher.
Findings
- The correlation coefficient between per capita Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) and minimum wage in Europe is -0.82.
- As the shadow economy increases in the continent, the minimum wage decreases.
- Luxembourg has the weakest shadow economy and the highest minimum wage.
- Albania has the lowest minimum wage and third strongest shadow economy.
- Ukraine has the second lowest minimum wage and the strongest shadow economy.
- Only Ukraine has a shadow economy that takes up more than half of its overall economy.
Caveats
- As always, correlation does not imply causation.
- Andorra, Austria, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Denmark, Finland, Switzerland, Iceland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Monaco, Moldova, Montenegro, the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia, Norway, Serbia, Russia, Sweden, Slovakia, San Marino, and Vatican City were missing data.
- Minimum wages sometimes vary by profession and other variables.
Details
Ukraine is the only outlier in this dataset and even if it were to be removed, the correlation between the two variables would still be pretty strong. There are three geographic clusters that show up: Balkan and Baltic countries are in the strong shadow economy and low minimum wage cluster, Western European countries are in the weak shadow economy and high minimum wage cluster, and Southern and Eastern European countries are clustered in the middle.
Unlike the Americas, there is a correlation between the strength of a shadow economy and the minimum wage but geography seems to also play a role.
Country Codes
| Code | Country | Annual Minimum Wage | Shadow Economy (as Percentage of GDP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AL | Albania | 4,790 | 34.6 |
| BE | Belgium | 20,056 | 21.9 |
| BG | Bulgaria | 7,867 | 35.6 |
| CZ | Czech Republic | 9,476 | 18.9 |
| DE | Germany | 22,236 | 15.8 |
| EE | Estonia | 9,170 | 31.4 |
| ES | Spain | 13,097 | 22.8 |
| FR | France | 20,081 | 14.9 |
| GB | United Kingdom | 18,577 | 12.5 |
| GR | Greece | 11,725 | 27.3 |
| HR | Croatia | 8,955 | 32.3 |
| HU | Hungary | 10,288 | 24.5 |
| IE | Ireland | 18,247 | 15.8 |
| LT | Lithuania | 8,421 | 32.4 |
| LU | Luxembourg | 24,024 | 9.8 |
| LV | Latvia | 7,647 | 29.5 |
| MT | Malta | 13,701 | 27.3 |
| NL | Netherlands | 20,340 | 13.1 |
| PL | Poland | 12,466 | 27.2 |
| PT | Portugal | 9,844 | 22.6 |
| RO | Romania | 8,994 | 32.5 |
| SI | Slovenia | 14,401 | 26.5 |
| UA | Ukraine | 7,303 | 50.4 |
Sources
US Department of State. 2017. "Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 2016." Accessed September 2, 2017. https://www.state.gov/j/drl/rls/hrrpt/humanrightsreport/index.htm#wrapper.
Schneider, Friedrich, Andreas Buehn, and Claudio E. Montenegro. 2010. "Shadow Economies All over the World: New Estimates for 162 Countries from 1999 to 2007." The World Bank Development Research Group.